HOW THE STARTING SYSTEM WORKS
To make an engine start, it must be turned at some speed so that it draws fuel and air into the cylinders and compresses it. The powerful electric starter motor does the turning. Its shaft carries a small ,pinion (gear wheel) which engages with a large gear ring around the rim of the engine flywheel. In a front-engine layout, the starter is mounted low down near the back of the engine. The starter needs a heavy electric current, which it draws through thick cables from the battery. No ordinary hand-operated switch could switch it on: it needs a large switch to cope with the high current. The switch has to be turned 'On and off very quickly to avoid dangerous, damaging sparking. For this reason, a solenoid is used - an arrangement in which a small switch activates a larger electromagnetic switch to complete the circuit. The ignition switch is usually worked by the ignition key. The driver turns the key beyond the 'ignition on' position to feed current to the solenoid.
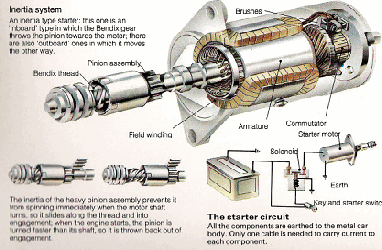
The ignition switch has a return spring which makes the switch spring back and turn the starter switch off as soon as the ignition key is released. When the switch feeds current to the solenoid, the electromagnet attracts an iron rod. The movement of the rod closes two heavy contacts, completing the circuit from the battery to the starter. The rod also has a return spring - when the ignition switch stops feeding current to the solenoid, the contacts open and the starter motor stops. The return springs are needed because the starter motor must not turn more than it has to in order to start the engine. The reason for this is partly that the starter uses a lot of electricity, which quickly runs down the battery. Also, if the engine starts and the starter motor stays engaged, the engine will spin the starter so fast that it may be badly damaged. The starter motor itself has a device, called a Bendix gear, which engages its pinion with the gear ring on the flywheel only while the starter is turning the engine.
The ignition switch has a return spring which makes the switch spring back and turn the starter switch off as soon as the ignition key is released. When the switch feeds current to the solenoid, the electromagnet attracts an iron rod. The movement of the rod closes two heavy contacts, completing the circuit from the battery to the starter. The rod also has a return spring - when the ignition switch stops feeding current to the solenoid, the contacts open and the starter motor stops. The return springs are needed because the starter motor must not turn more than it has to in order to start the engine. The reason for this is partly that the starter uses a lot of electricity, which quickly runs down the battery. Also, if the engine starts and the starter motor stays engaged, the engine will spin the starter so fast that it may be badly damaged. The starter motor itself has a device, called a Bendix gear, which engages its pinion with the gear ring on the flywheel only while the starter is turning the engine.
The engine does not crank and the starter does not work. Tracing why the starter motor does not work is simple and straightforward. Turn the headlights on. If they are dull the battery is discharged.If the headlights are bright - but dim noticeably as the starter switch is engaged - observe whether, and how quickly, they regain their full brightness once the starter switch is released. A slow recovery, or no recovery, indicates a defective battery. if the recovery is immediate, a poor connection on the main battery cables is indicated. With the vehicle gearbox put in neutral, have a helper engage the starter switch while you jam the blade of a screwdriver between a . battery post and the terminal on the battery cable - do each post in turn. The starter will respond immediately the poor connection is found. Remove the battery cable and clean it thoroughly. A jammed starter motor may also cause the head lamps to dim..
Usually this will be accompanied by an"audible click - especially on older, inertia-type starter motor systems - as the solenoid engages. With pre-engaged starter motors, the solenoid may be relatively silent but it will be noted that the return spring for the actuating arm is almost fully compressed. A further clue in deciding on whether the starter motor is probably jammed is to observe the fan blades as the solenoid clicks in.
If they do not move even slightly, the starter motor is probably jammed - if it is, check whether there is a square stub situated on the end of the armature shaft. If so, turn it with a spanner to free the pinion. If not - and the car has manual transmission - place the vehicle in one of its lower gears.
If they do not move even slightly, the starter motor is probably jammed - if it is, check whether there is a square stub situated on the end of the armature shaft. If so, turn it with a spanner to free the pinion. If not - and the car has manual transmission - place the vehicle in one of its lower gears.
With the ignition off, release the handbrake and rock the car repeatedly forward and back until the pinion frees itself. If the car has automatic transmission, loosen the starter mounting bolts and shake the starter pinion free. On very rare occasions, it may be found that although the solenoid is clicking, the heavy-duty contacts within the solenoid itself are burnt and not providing electrical contact. Or, alternatively, there is poor contact between the brushes in the starter motor and the commutator. If the battery is in order but the solenoid does not click when the starter switch is engaged, either the solenoid, the wiring to the solenoid or the starter switch is faulty. In such instances the headlamps will not dim. Check the solenoid switch by tracing the low-tension LTI wire,which leads back to the ignition switch. To activate the solenoid (depending on its type) this, contact has to have current applied to it, or - on some older' vehicles - it may have to be earthed. Begin by earthing this contact and then bridging it to the nearby battery power lead. If the solenoid does not respond, it is faulty. Alternatively the fault will either be found in the ignition switch or the wire itself. (Note: the solenoid switch can be by- passed by temporarily bridging its main terminals with a well- insulated screwdriver.
Checking and replacing the starter motor
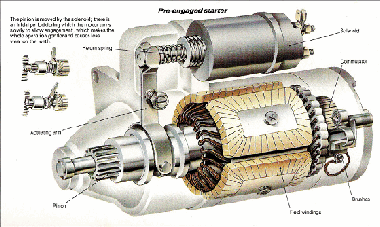
Starter CircuitIf testing the starter circuit in-dicates a fault in the starter motor, disconnect the battery and remove the motor from the car - complete with its attached solenoid if it is a pre-engaged type. To trace the fault and carry out repairs, you will nearly always have to strip down the motor, especially if the fault is in the commutator or brush gear. However, the Bendix gear of an inertia- type starter can be repaired without stripping; removing the motor from the car gives sufficient access. Some faults, such as a badly worn commutator, are beyond repair and you have to buy a new armature. However, you can renew worn bearings repair a solenoid ; fit new brushes in the commutator to replace worn ones and repair minor damage to the commutator.
Damage to the electrical windings is usually too difficult to deal with at home. An auto-electrician can cure armature short circuit in the field coils, but anything else calls for fitting new components. A single fault in the motor is probably worth repairing, but if you find more than one fault, check the cost of all the spares you need. You may find it cheaper - and quicker - to replace the motor with another one.
Starter CircuitIf testing the starter circuit in-dicates a fault in the starter motor, disconnect the battery and remove the motor from the car - complete with its attached solenoid if it is a pre-engaged type. To trace the fault and carry out repairs, you will nearly always have to strip down the motor, especially if the fault is in the commutator or brush gear. However, the Bendix gear of an inertia- type starter can be repaired without stripping; removing the motor from the car gives sufficient access. Some faults, such as a badly worn commutator, are beyond repair and you have to buy a new armature. However, you can renew worn bearings repair a solenoid ; fit new brushes in the commutator to replace worn ones and repair minor damage to the commutator.
Damage to the electrical windings is usually too difficult to deal with at home. An auto-electrician can cure armature short circuit in the field coils, but anything else calls for fitting new components. A single fault in the motor is probably worth repairing, but if you find more than one fault, check the cost of all the spares you need. You may find it cheaper - and quicker - to replace the motor with another one.
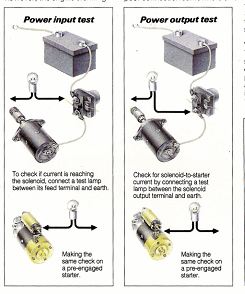
Remember that a test lamp is useful not only to check whether particular component is, or becomes, live - but can also be used instead of an ohmmeter to find high resistance points and poor connections. For example, if a test lamp that is made from a headlamp or similar globe were to be connected in series with any other circuit, the test lamp would light up if there was a high resistance in the circuit, since current always tries to find the path of least resistance.
Download this guide, instructions to fix or replace starters/alternators. Checking of battery are also presented.
Gratis Diens Kwotasie


